Diabetic Retinopathy
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
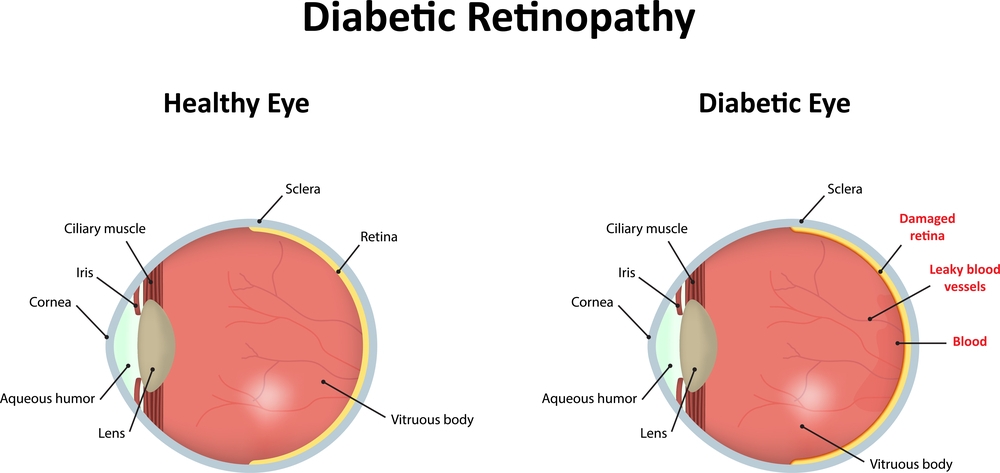
Diabetic Retinopathy, as the name suggests is a condition that occurs in people with diabetes. It leads to progressive damage to the retina (the light-sensitive lining at the back of the eye). Diabetic Retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that poses a threat to the sight.
Diabetes interferes by disturbing the body’s ability to use and store sugar (glucose). The disease is marked by the presence of too much sugar in the blood, which can cause damage to many body organs, including the eyes. With time, diabetes damages the blood vessels in the retina. Diabetic Retinopathy occurs when these tiny blood vessels leak blood and other fluids. The leakage causes the retinal tissue to swell, resulting in cloudy or blurred vision. The condition usually affects both eyes. The longer a person has diabetes, the higher the likelihood of the person to develop diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic Retinopathy can cause blindness, if left untreated.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy include:
- Seeing spots or floaters
- Blurred vision
- Having a dark or empty spot in the centre of the vision
- Difficulty seeing properly at night
